Las Vegas Sands is a gambling colossus with a 30+ year history that can be as attractive to investors as it is repulsive. Like Casanova in a fancy suit, it can impress with its spectacular casinos and hotels, but underneath the glitz is a financially challenged and heavily indebted colossus with a fickle track record. Its fate is closely intertwined with investor confidence, the attendance at extravagant resorts and the development of a pandemic. Let's take a look.

Las Vegas Sands is an American company that operates casinos and hotels. It was founded in 1988 by Sheldon Adelson and is one of the largest resort and casino operators in the world.
The company currently operates 6 integrated resorts - 3 in Macau, 2 in Singapore and 1 in Las Vegas, employing approximately 50,000 people worldwide. The key market for Las Vegas Sands is Macau, where it owns the majority of its casinos. The company has a strong position and is the market leader in this market with a market share of around 35%. Its main competitors include MGM Resorts, Wynn Resorts and Galaxy Entertainment Group.
The competitive advantage of Las Vegas Sands is its brand, extensive industry experience, quality of service and uniqueness of its resorts. Risks include a slowing Chinese economy, possible stricter gaming regulations in the future and competition.
Going forward, the company plans further expansion in Asia, particularly in Japan, South Korea and Vietnam. It is also investing in developing existing resorts and improving the guest experience. The aim is to maintain its leading position among gaming business operators and to grow steadily.
From the above, Las Vegas Sands is a highly successful company with a history of over 30 years, a strong position in key markets, particularly in Asia, and plans for further growth. However, its business is dependent on the gambling business, which poses some risk.

Las Vegas Sands differentiates itself from its competitors in several ways:
1. Brand and prestige: Las Vegas Sands is the operator of the largest and most prestigious integrated gaming and entertainment resorts in the world. Its Venetian Macao, Marina Bay Sands in Singapore and The Venetian Las Vegas are world-renowned and attract the wealthiest clientele. This prestige and status allows them to charge higher prices and margins.
2. Quality and variety of services: LVS resorts offer world-class accommodation, restaurants, shopping, spa and entertainment. It's not just a classic casino, but an entire luxury resort experience. This ensures customer loyalty and higher spending.
3. Asian expansion: Unlike most competitors, LVS has focused on expansion in Asia, especially in Macau and Singapore. This has allowed it to grow rapidly and diversify outside of Las Vegas. Asia presents enormous potential, but also risks such as regulation and a slowing Chinese economy.
4. Generous investment: LVS is continuously investing massively in the development and innovation of existing resorts. This ensures first-class service, unique attractions and re-engaging customers. On the other hand, it reduces profits and increases costs.
5. The downside - Debt: Unlike most competitors, LAS has a high proportion of debt financing. This allows for faster growth but increases financial risk in the event of a decline in sales. Stable access to the bond markets is therefore key.
Finance
Total revenues are around USD 13-14 billion per year. In 2020, they dropped by 18% due to the COVID-19 pandemic and the closure of casinos and resorts. However, they have partially recovered to USD 4.1 billion in 2021, but are still 11% lower than pre-pandemic levels.
Cost of sales are around 50-60% of revenue. Operating costs are high, around USD 10 billion per year. This leads to an operating loss of USD 1.6 billion in 2020.
Net profit is highly volatile, reaching almost USD 3 billion in 2018 and 2019, but the company reports a net loss of almost USD 1 billion in 2020 and a profit of USD 1.8 billion in 2021.
The results show that the Las Vegas Sands business is very costly and profits depend on high casino and resort attendance. In times of crisis, such as the COVID pandemic, the company generated high losses. On the other hand, in years of growth, it can generate very solid profits and cash flow.
Balance Sheet
Total assets are around USD 20-23 billion. In 2020, it declined by 11% due to the reduction in cash and receivables as a result of the pandemic. However, in 2021 it partially increased to USD 22 billion due to bond issuance and increase in cash.
Total liabilities have reached USD 16-18 billion in recent years. This is mainly long-term debt, which rises to USD 15 billion in 2020. Net debt (net of cash) has been in the range of USD 9-13 billion in recent years.
Equity is relatively low, at around USD 3.5-6.5 billion. In 2020, it even dropped by 45% to USD 2.2 billion due to a reported loss. And in 2021, it partially recovered to USD 3.7 billion.
Working capital is low and volatile, even negative in 2020. This points to the need for external financing of operations. Overall, the results suggest that the capital structure of Las Vegas Sands is highly leveraged with a high proportion of foreign capital. The company is dependent on access to external financing, either debt or equity.
High debt carries risk in the event of a decline in sales and profits. On the positive side, most of the debt is long-term, which provides financial flexibility. The cash position has improved in recent years, which is also positive. However, it would be ideal to strengthen equity and reduce the share of foreign capital. Overall, the capital structure of Las Vegas Sands can be considered risky, however, given the nature of the industry and the complexity of the business, some level of debt is inevitable.
Cash Flow
Operating cash flow is volatile. It reached USD 3 billion in 2019, but fell into negative territory to USD -1.3 billion in 2020 due to a decline in sales. It was negative again in 2022 (-795m USD).
Investment cash flow is also volatile. Last year it reached USD 4.2bn due to asset sales, but in previous years it was rather negative due to high investments.
Financial cash flow is positive, which shows that the company is dependent on external financing. In recent years, it has issued bonds worth up to USD 4 billion a year.
Free cash flow is also volatile and was negative in 2020-2021, indicating problems in generating cash from operations (again, these were pandemic problems).
The results show that the ability to generate cash from operations and fund investments is problematic for Las Vegas Sands, especially in a downturn and crisis. The company is therefore dependent on access to external capital, which poses a risk.
The market capitalisation is USD 47 billion. Shares have risen by more than 65% over the past year, reflecting investors' positive expectations of the company's recovery from the pandemic.
However, the company does not pay a dividend, reinvesting all profits in business development. The P/E ratio is not relevant as the company has not posted a positive net profit in the last one year. However, it is forecast to recover profitability relatively quickly. Forward P/E of 21 indicates relatively high growth expectations going forward.
Overall, debt is at a relatively high level, with a debt-to-equity ratio of 4.12. However, most of the debt is long-term. But the indicators are not very indicative at the moment, just as we see unflattering figures for P/B ratios, P/S, ROE, ROA, ROI and margins, we have to take into account that the company has been crippled by the pandemic for the last few years and is only just getting back on course.
Analyst expectations
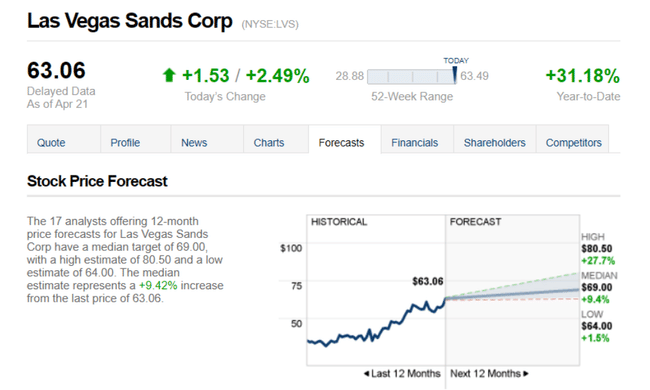
The 17 analysts offering 12-month price forecasts for Las Vegas Sands Corp have a median target of 69.00, with a high estimate of 80.50 and a low estimate of 64.00. The median estimate represents an increase of +9.42% from the last price of 63.06.
- What do you think about the company? 🤔
Please note that this is not a financial advisory service. Every investment must go through a thorough analysis.
Las Vegas Sands: gambling colossus seeks return to prosperity after challenging pandemic