Economists predict the Fed will raise rates by another quarter percentage point to bring inflation under control this spring. There would be nothing so special about that. That's probably what everyone expects. But then, they say, the hikes will stop for good. What would that mean?

Rates are already the highest they have been in 15 years, having risen gradually from near-zero levels a year ago to 5%. The Fed has cited persistent inflation in making its decision and has already hinted that it may allow one more hike before it levels off.
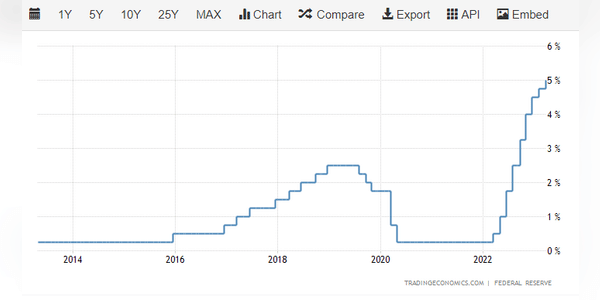
At an event in Washington D.C. Kathy Bostjancic, Nationwide Bank's chief economist, said, "The expectation at the moment is that rates will rise: "One more rate hike makes sense, especially if the financial crisis doesn't spread."
Her words were backed up by Lydia Boussour, chief economist at consultancy EY-Parthenon, who said: "We expect the Fed to raise rates…